When building powerful and efficient Power BI reports, your data model is everything. The way your data is structured affects performance, usability, and accuracy. Two of the most common modeling approaches in Power BI are the Star Schema and the Snowflake Schema. Understanding the difference between these two can help you design models that are not only faster but also easier to maintain and scale.
Read More: Choosing the Right Design in Power BI: Star Schema vs. Snowflake
In this post, we’ll break down what each schema is, when to use them, and which one works best for your Power BI projects.
What Is a Star Schema?
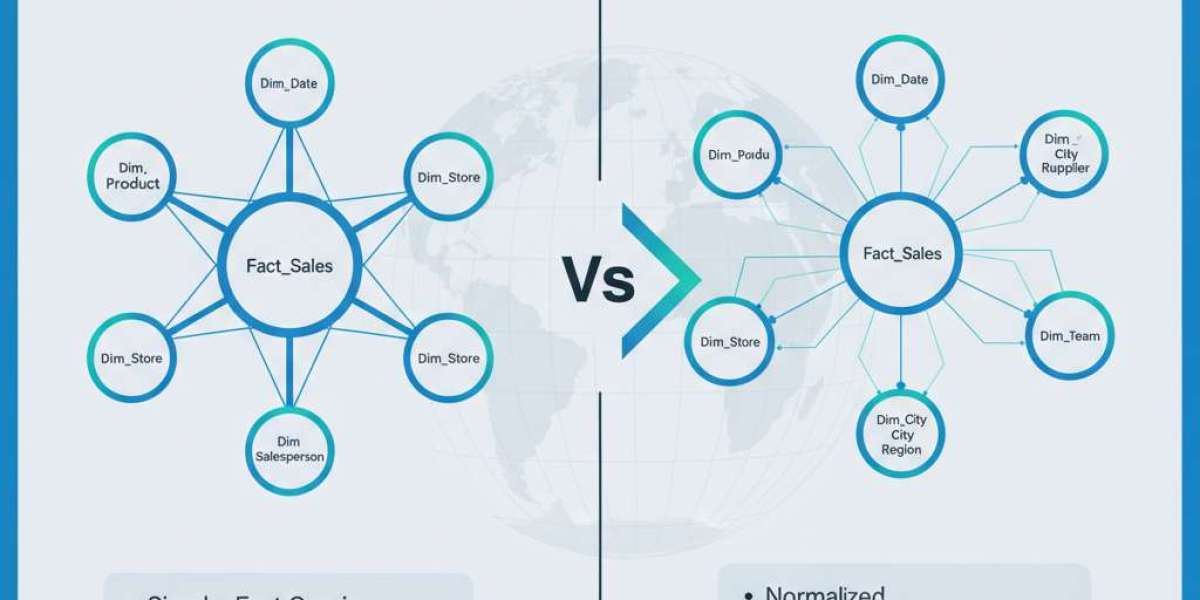
A Star Schema is the most widely recommended data modeling structure for Power BI. It gets its name from the star-like shape that forms when you map out the tables. At the center of the star is a fact table, which contains the key metrics or numerical data (such as sales, revenue, or quantity). Surrounding the fact table are dimension tables, which hold descriptive information (such as product names, customers, dates, or regions).
Example of a Star Schema
Fact Table: Sales (includes metrics like Sales Amount, Quantity, and Profit)
Dimension Tables: Date, Customer, Product, Region
These dimension tables connect directly to the fact table using simple, one-to-many relationships.
Advantages of a Star Schema
High performance: Fewer joins between tables make queries faster.
Simpler relationships: Easy to understand for both developers and business users.
Optimized for DAX calculations: Power BI’s engine works best with this model.
Cleaner visuals: Reduces model complexity, making it easier to navigate and maintain.
What Is a Snowflake Schema?
A Snowflake Schema is a more normalized version of the star schema. It breaks dimension tables into additional sub-tables to remove redundancy. The structure resembles a snowflake, where each dimension table can connect to multiple related tables.
Example of a Snowflake Schema
Fact Table: Sales
Dimension Tables: Product → Category → Department → Customer → Geography → Region
In this design, dimensions are split into multiple related tables rather than a single flat table.
Advantages of a Snowflake Schema
Reduced data redundancy: Helps minimize duplicate information across tables.
More accurate relationships: Useful when dimensions are shared across multiple fact tables.
Better data organization: Helpful when working with very large, complex datasets.
Star Schema vs. Snowflake Schema: Key Differences
| Feature | Star Schema | Snowflake Schema |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Simple and denormalized | Complex and normalized |
| Performance | Faster queries | Slower queries due to more joins |
| Ease of use | Easier to understand | More difficult for end users |
| Storage efficiency | Slightly higher redundancy | Lower redundancy |
| Power BI compatibility | Highly optimized | Can cause performance issues |
Which Schema Should You Use in Power BI?
While both schemas have their uses, Microsoft recommends the Star Schema for most Power BI models. It strikes the right balance between performance and simplicity.
Here’s why the Star Schema is the better choice in most scenarios:
Optimized for Power BI’s VertiPaq engine – Power BI compresses and queries data more efficiently in star schemas.
Simpler DAX formulas – You’ll write cleaner, faster, and more accurate calculations.
Better user experience – Report designers and end users find it easier to navigate a straightforward model.
Faster refresh and load times – Since fewer joins are required, queries execute more quickly.
However, a Snowflake Schema might be suitable if:
You’re working with shared dimension hierarchies across multiple models.
Your dataset is very large and normalized in the source system.
You need to maintain data consistency across enterprise systems.
Visit Here: https://www.fusion-institute.com/building-better-models-in-power-bi-star-schema-or-snowflake
Final Thoughts
When it comes to Power BI, the Star Schema is almost always the best choice. It simplifies your model, improves report performance, and makes DAX calculations more manageable. Snowflake schemas have their place in certain enterprise environments, but for most Power BI projects, keeping it simple wins every time. The key takeaway? Design your Power BI models with a clear, star-shaped structure—you’ll thank yourself later when your reports load fast, your relationships make sense, and your insights shine.