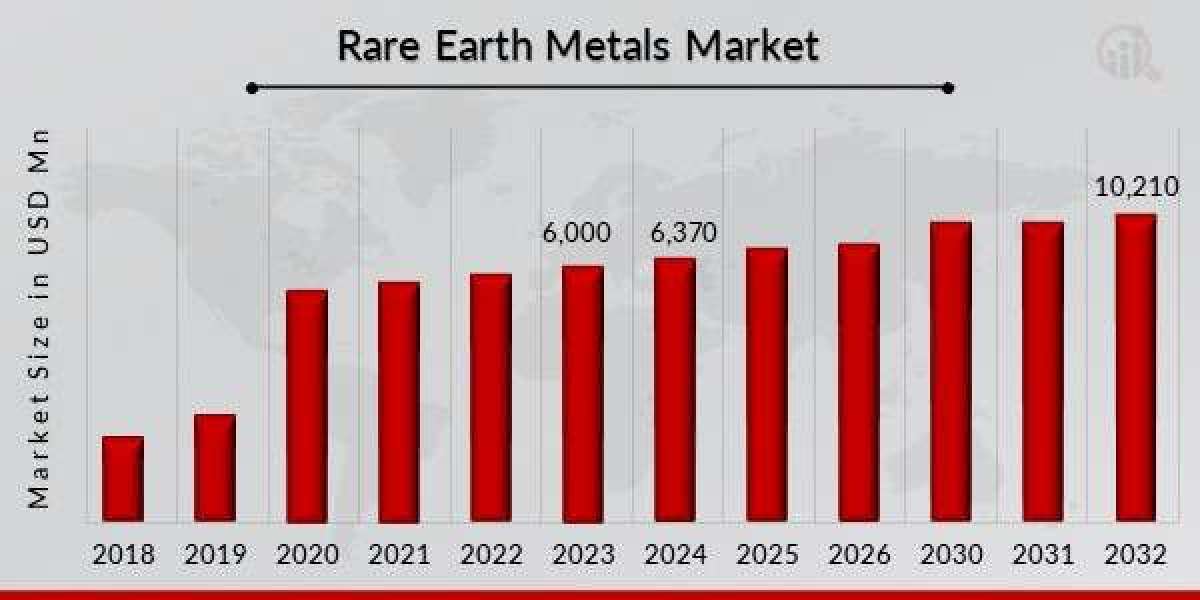
The rare earth metal market has emerged as one of the most crucial and strategically important sectors in the global economy. These metals, although found in relatively small concentrations across the Earth’s crust, play a vital role in modern technology, energy solutions, and advanced manufacturing. The demand for these metals has increased dramatically as industries worldwide embrace innovation, sustainability, and technological transformation. Understanding the dynamics of this market requires examining its composition, applications, and the broader economic factors that shape its growth trajectory.
Rare earth metals consist of 17 elements that include lanthanum, cerium, neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, among others. Despite being referred to as “rare,” these elements are not exceedingly scarce, but they are often found in dispersed forms that make extraction and refining complex. Their unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties make them indispensable in a wide range of applications. From the smartphone in a consumer’s hand to the electric vehicle on the road, rare earth metals are woven into the fabric of daily life, often unnoticed yet highly significant.
One of the strongest drivers of the rare earth metal market is the rising adoption of clean energy technologies. Wind turbines, for example, rely on powerful magnets made from neodymium and dysprosium to generate renewable power efficiently. Similarly, the booming electric vehicle industry depends heavily on rare earth elements for batteries, motors, and lightweight components. As governments and organizations worldwide commit to carbon neutrality and sustainability, the reliance on these metals becomes even greater, positioning them as the backbone of the green energy revolution.
Consumer electronics also account for a large share of demand. Laptops, televisions, headphones, and smartphones all incorporate rare earth metals for screens, batteries, and sound systems. The global appetite for advanced electronic gadgets continues to expand, particularly in emerging markets where technological adoption is rapid. This creates consistent pressure on the rare earth supply chain, encouraging mining companies and manufacturers to increase output and explore new deposits.
The defense and aerospace sectors further highlight the importance of rare earth metals. Advanced weaponry, precision-guided missiles, jet engines, and satellite systems require specific rare earth elements to function reliably. Their role in national security makes them not just commodities but also strategic assets. Many governments consider rare earth supply chains as critical infrastructure, leading to efforts aimed at securing long-term availability and minimizing reliance on a small number of producing countries.
Geographically, the rare earth metal market is highly concentrated. A few nations dominate production, with significant reserves located in Asia and parts of Africa. This concentration often leads to geopolitical tensions and discussions around supply chain stability. Countries dependent on imports are investing in recycling technologies, alternative materials, and domestic mining projects to mitigate risks. At the same time, producing nations are strengthening their control over exports, recognizing the immense value of these resources in global trade.
Technological advancements in mining and refining processes are reshaping the market. Traditional extraction methods are being supplemented with more sustainable and efficient approaches aimed at reducing environmental impacts. Since rare earth mining can involve significant ecological challenges, companies are increasingly expected to adopt responsible practices that balance profitability with environmental stewardship. This trend aligns with broader societal expectations, where industries are judged not only by their output but also by their contribution to sustainable development.
Pricing in the rare earth metal market remains volatile, influenced by supply-demand imbalances, political decisions, and technological breakthroughs. When supply chains are disrupted, prices can spike sharply, affecting industries downstream that rely on stable input costs. Conversely, new discoveries or expanded production capacity can ease market pressures, though the long lead times associated with rare earth projects mean that adjustments are rarely immediate. Investors and companies must therefore navigate a landscape that is both opportunity-rich and risk-prone, where careful strategy is essential.