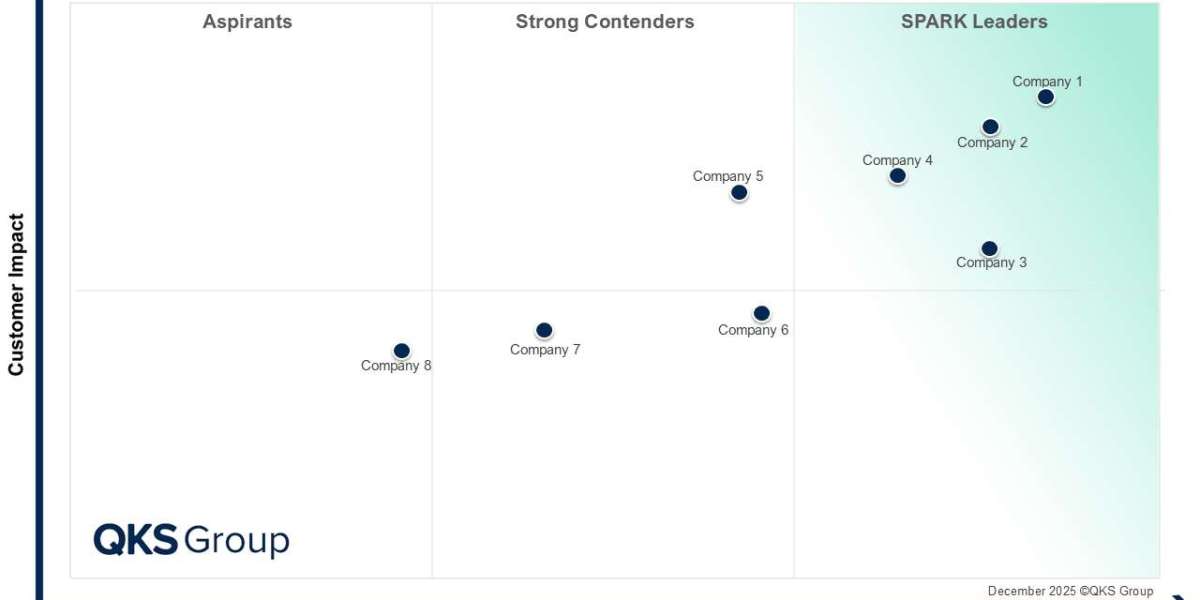
Introduction
As digital services become more latency-sensitive, data-intensive, and distributed, the edge of the network has emerged as a critical point of differentiation for telecom operators. From immersive media and smart manufacturing to private 5G and mission-critical enterprise applications, success increasingly depends on where and how computing resources are deployed. In this context, Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) Solutions – Infrastructure-Led Providers play a foundational role. These vendors are shaping the core edge infrastructure that enables communication service providers (CSPs) to move beyond connectivity and unlock new revenue opportunities.
Market / Industry Overview
Multi-Access Edge Computing represents the convergence of telecom networks and cloud computing, bringing compute, storage, and application hosting closer to end users and devices. While multiple ecosystems participate in the MEC value chain, infrastructure-led providers—traditionally Network Equipment Providers (NEPs)—form the backbone of telco-grade edge deployments.
These vendors deliver end-to-end MEC platforms built on their own network infrastructure, software stacks, and orchestration frameworks. Their solutions tightly integrate radio access networks (RAN), transport, and core network intelligence with edge computing capabilities. This deep integration is essential for achieving deterministic latency, traffic steering, service assurance, and carrier-grade reliability.
For CSPs, infrastructure-led MEC solutions are strategically important. They enable operators to extend network capabilities into distributed edge locations, support both public and private networks, and retain architectural control while scaling new services. As edge computing moves from experimentation to commercialization, this segment has become central to long-term telecom transformation strategies.
Key Challenges Businesses Face
Despite growing interest and investment, CSPs and enterprises face several challenges when deploying MEC at scale:
- Complex network integration across RAN, transport, core, and edge compute layers
- Latency and performance assurance for mission-critical applications
- Operational complexity in managing distributed edge infrastructure
- Fragmented ecosystems and evolving standards
- Security and data sovereignty concerns at the edge
- Unclear monetization paths for edge-based services
Infrastructure-led providers address many of these challenges by embedding MEC capabilities directly into the network fabric, reducing integration friction and operational risk.
Key Trends & Innovations
The evolution of MEC infrastructure is being shaped by several important trends:
- 5G Standalone (SA) and UPF Integration
MEC platforms are increasingly integrated with 5G core functions, including User Plane Function (UPF), enabling local breakout, traffic optimization, and network slicing. - Cloud-Native Telco Architectures
Containerized network functions, Kubernetes-based orchestration, and microservices are becoming standard across MEC platforms. - AI-Driven Network and Edge Automation
AI and analytics are used for traffic steering, fault detection, predictive scaling, and performance optimization at distributed edge sites. - Private 5G and Enterprise Edge
Infrastructure-led providers are extending MEC platforms to support private networks for manufacturing, logistics, ports, and campuses. - Integrated Edge Orchestration
Unified orchestration across network, compute, and applications simplifies lifecycle management and service assurance.
These innovations are strengthening the role of Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) Solutions – Infrastructure-Led Providers as enablers of scalable, carrier-grade edge environments.
Benefits & Business Impact
Infrastructure-led MEC platforms deliver tangible value for CSPs and enterprises:
- Ultra-low latency and deterministic performance through tight network integration
- Improved ROI by leveraging existing telecom infrastructure investments
- Faster service rollout with pre-integrated edge architectures
- Operational efficiency via unified orchestration and automation
- Scalability across thousands of distributed edge locations
- Enhanced security and compliance aligned with telco-grade standards
- New monetization opportunities through edge-enabled enterprise and vertical services
For CSPs, these benefits translate into differentiation beyond connectivity and stronger positioning in enterprise digital transformation initiatives.
Use Cases or Real-World Examples
Infrastructure-led MEC solutions support a wide range of real-world use cases:
- Smart Manufacturing: Real-time control, machine vision, and robotics powered by private 5G and on-premise edge compute.
- Media and Entertainment: Low-latency video processing, AR/VR streaming, and immersive fan experiences.
- Transportation and Logistics: Edge-based analytics for traffic management, ports, and autonomous operations.
- Public Safety and Smart Cities: Video analytics, emergency response, and critical communications at urban edge nodes.
- Energy and Utilities: Edge intelligence for grid monitoring, predictive maintenance, and operational safety.
In each case, infrastructure-led providers enable CSPs to host and manage edge applications with carrier-grade performance and reliability.
How Organizations Can Choose the Right Solution
Selecting the right MEC infrastructure partner is a strategic decision. CSPs and enterprises should evaluate vendors based on:
- Depth of 4G/5G network integration
- Maturity of MEC and edge orchestration platforms
- Support for public and private network deployments
- Cloud-native readiness and openness
- Security, resilience, and compliance capabilities
- Ecosystem partnerships and application enablement
- Proven ability to support service monetization
The most effective providers combine strong infrastructure foundations with a clear roadmap for edge innovation and commercialization.
Future Outlook (2025–2028)
Between 2025 and 2028, infrastructure-led MEC platforms will continue to evolve as 5G SA adoption accelerates and enterprise demand for real-time services grows. Expect tighter integration between network and compute layers, broader use of AI for autonomous edge operations, and increased alignment with vertical-specific requirements.
CSPs will increasingly rely on Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) Solutions – Infrastructure-Led Providers to scale edge services profitably, support hybrid public-private network models, and compete with hyperscalers while retaining network control.
Conclusion
Multi-Access Edge Computing is redefining the role of telecom networks in the digital economy. Infrastructure-led providers form the backbone of this transformation by delivering telco-grade MEC platforms that integrate network intelligence with distributed compute. For CSPs seeking to monetize edge investments and enterprises demanding predictable performance, these providers offer the scale, reliability, and control required to turn edge computing into a sustainable business advantage.