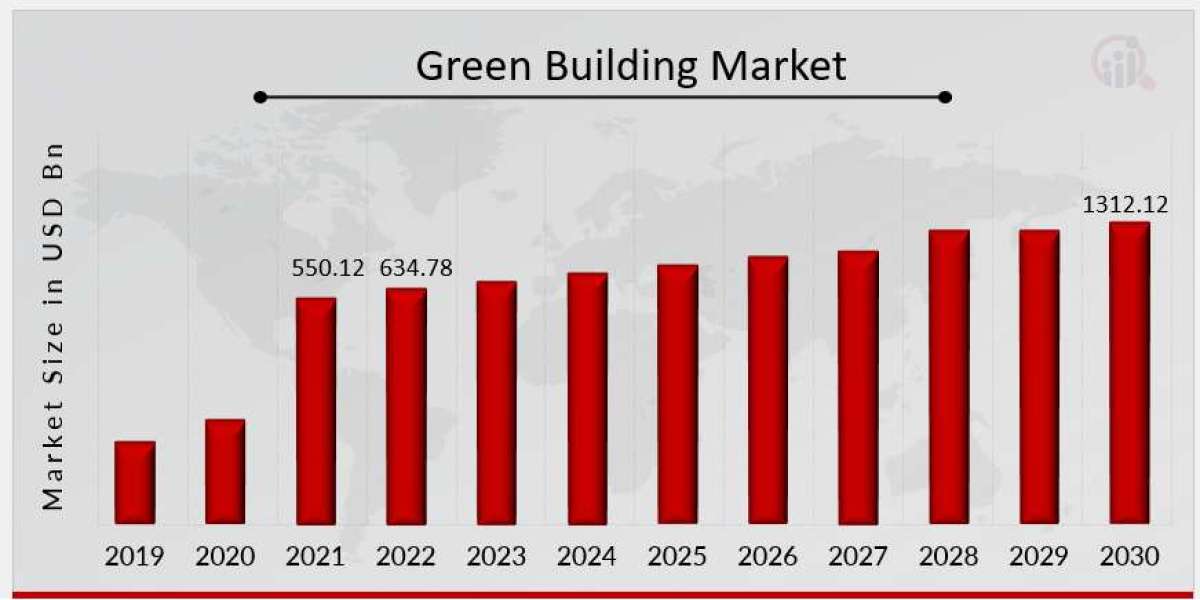
The green building market has emerged as one of the most transformative movements within the construction and real estate sector, reshaping the way spaces are designed, built, and utilized. Unlike conventional building practices, green building focuses on sustainability, efficiency, and harmony with the natural environment. This market has steadily grown as developers, architects, governments, and end-users recognize the value of structures that minimize environmental impact, optimize energy and water use, and create healthier living and working environments.
At its core, the green building market revolves around the concept of reducing the ecological footprint of construction activities and the ongoing operation of buildings. It emphasizes the use of eco-friendly materials, advanced construction technologies, and innovative design strategies that promote energy efficiency and resource conservation. For instance, integrating natural light, ventilation, renewable energy sources like solar or wind, and water recycling systems are common practices that have become hallmarks of the industry. As populations grow and urbanization accelerates, the need for environmentally responsible infrastructure has become more urgent, fueling demand for green building solutions.
One of the driving forces behind the green building market is the increasing awareness of climate change and the pressing need to mitigate carbon emissions. Buildings contribute significantly to global greenhouse gas emissions through energy consumption, heating, cooling, and construction materials. By adopting green building practices, stakeholders can drastically reduce energy consumption, lower reliance on fossil fuels, and create spaces that support long-term environmental goals. This aligns with the broader global push toward achieving sustainability targets and reducing the adverse effects of human activity on ecosystems.
The market also benefits from the economic advantages associated with sustainable construction. While the initial investment in green technologies, eco-friendly materials, and certifications may be higher compared to traditional methods, the long-term savings are substantial. Green buildings typically incur lower operational costs due to reduced energy and water consumption. They also require less maintenance over time because of their emphasis on durable, high-quality materials. For homeowners and tenants, this translates into reduced utility bills, while for commercial developers, it means higher property values and improved return on investment. Consequently, the market for green buildings has been gaining momentum not just as an environmental necessity but also as a financially viable approach.
Health and wellness have become integral aspects of the green building movement. Unlike conventional buildings that may rely heavily on artificial lighting, synthetic materials, and mechanical ventilation, green buildings prioritize natural light, improved air circulation, and the use of non-toxic materials. These features have been shown to improve occupant well-being, productivity, and overall satisfaction. In office spaces, this translates into better employee performance and reduced absenteeism, while in residential spaces it ensures healthier and more comfortable living conditions. The market has responded to this shift by integrating wellness-focused designs into projects, making green buildings attractive for both residential and commercial buyers.
Urbanization, particularly in developing countries, has created significant opportunities for the green building market. Rapid construction activity in cities often puts immense pressure on natural resources, leading to pollution, deforestation, and energy shortages. Green building practices offer a pathway to balance the need for urban development with environmental preservation. By adopting sustainable designs, cities can reduce heat islands, improve waste management, and provide infrastructure that supports long-term growth. Governments in many regions are encouraging this shift by offering tax benefits, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks that reward sustainable construction. Such initiatives have created an enabling environment for the green building market to flourish.
Technology has also played a pivotal role in shaping the market. The rise of smart building systems, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and advanced building information modeling (BIM) tools has made it easier for architects and engineers to incorporate sustainable features into projects. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring of energy usage, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource allocation, which enhances the overall sustainability of structures. Furthermore, innovations in materials, such as recycled composites, energy-efficient glass, and low-carbon cement, have expanded the possibilities of green construction. As technology continues to evolve, the market is expected to experience even greater advancements, making green buildings more accessible and efficient.
Another important factor driving the green building market is the changing consumer mindset. Modern buyers and tenants are increasingly conscious of their environmental footprint and prefer living or working in spaces that reflect their values. For younger generations, sustainability is not just a trend but a lifestyle choice, and green buildings align with this preference. Developers and real estate companies have recognized this shift, often highlighting the sustainable features of their projects as key selling points. This cultural transformation is likely to sustain demand for green buildings in the years ahead, making the market not just a niche but a mainstream necessity.
On a global scale, the green building market is not confined to urban skyscrapers or high-end residential projects. Rural communities, educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and industrial complexes are also adopting sustainable construction practices. This widespread adoption underscores the versatility of green building principles, which can be tailored to diverse contexts and budgets. From small eco-friendly homes to large commercial complexes, the market has demonstrated that sustainability can be integrated into all scales of construction.