Roller ball bearings are among the most essential components in mechanical engineering, used to reduce friction and support rotating parts. Whether it’s in cars, manufacturing machines, or aerospace systems, these tiny parts carry big responsibilities.
In this article, you’ll understand what a roller ball bearing is, how it functions, and where it’s used in real-world industries.
What Is a Roller Ball Bearing?
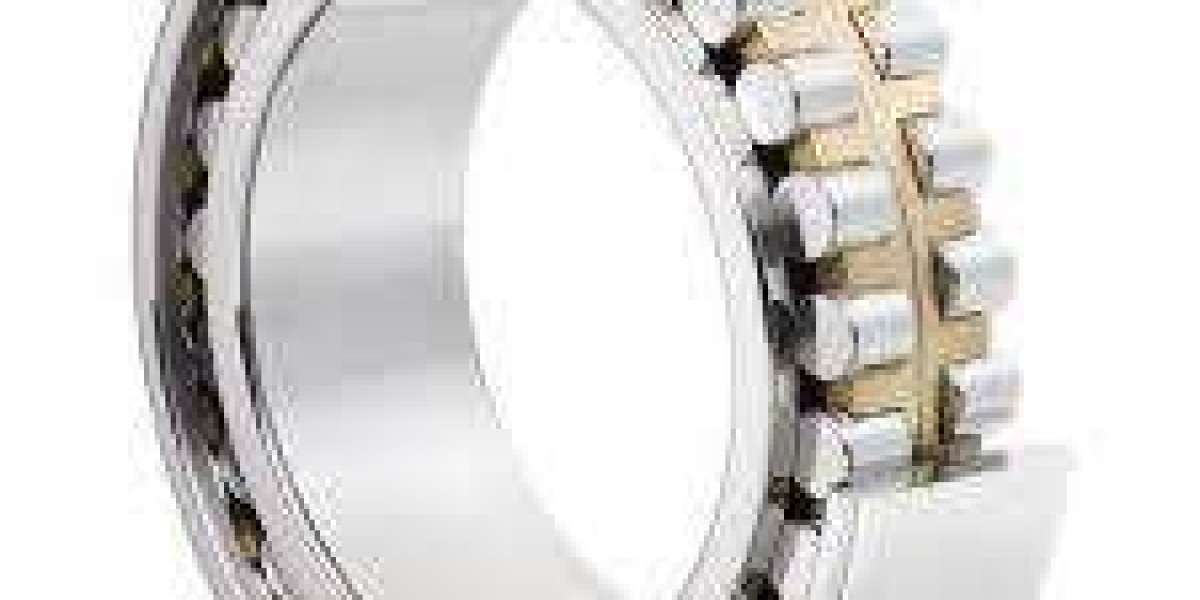
A roller ball bearing is a type of anti-friction bearing that uses small, hardened steel balls (or rollers) between inner and outer rings to reduce rotational resistance. These bearings are designed to handle both radial and axial loads efficiently.
Roller ball bearings allow components to move smoothly with minimal effort, thus reducing wear and increasing the machine's life span.
How Does a Roller Ball Bearing Work?
The basic structure of a roller ball bearing includes:
Inner Ring – Attached to the rotating shaft
Outer Ring – Held in place within the housing
Balls or Rollers – Between the two rings
Cage – Maintains spacing between the rolling elements
When the shaft rotates, the balls rotate too, reducing the surface contact between moving parts. This minimizes friction, heat buildup, and energy loss, making machines operate efficiently.
Types of Roller Ball Bearings
There are several types of roller ball bearings designed for different loads and applications:
1. Deep Groove Ball Bearings
These are the most common type. Suitable for high-speed applications, they handle both radial and axial loads.
2. Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Designed to handle higher axial loads, often used in high-performance engines and gearboxes.
3. Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Useful where misalignment is a factor, such as in agricultural machinery.
4. Thrust Ball Bearings
Used for low-speed axial load applications like turntables or low-speed shafts.
Key Benefits of Roller Ball Bearings
Using a roller ball bearing in machinery offers several benefits:
Low Friction: Helps improve energy efficiency
High Load Capacity: Supports both radial and axial forces
Compact Design: Saves space without compromising strength
Long Lifespan: With proper maintenance, they offer extended operational life
Versatile Applications: Fit for everything from skateboards to turbines
Common Applications in Various Industries
Roller ball bearings are used in almost every mechanical system. Below are some notable sectors:
1. Automotive Industry
Used in wheels, gearboxes, transmissions, and engines.
2. Aerospace Engineering
Applied in turbines, gyroscopes, and control surfaces.
3. Manufacturing and Machinery
Key in conveyor belts, motors, and production line equipment.
4. Home Appliances
Fans, washing machines, and even blenders use these bearings.
5. Medical Equipment
In diagnostic devices, pumps, and precision instruments.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Use
To extend the life of your roller ball bearing:
Keep them clean and well-lubricated.
Avoid overloading beyond their rated capacity.
Inspect for noise, heat, or vibration regularly.
Replace worn-out bearings promptly to avoid machinery failure.
Why Choosing the Right Bearing Matters
A poor-quality bearing can lead to overheating, system failure, or even hazardous accidents. Always choose roller ball bearings from trusted suppliers who offer reliable specifications and materials.
Final Thoughts
From the smallest gadget to the largest industrial machine, roller ball bearings play a vital role in keeping things moving. Knowing their structure, types, and applications helps you make informed choices for your equipment or business needs.
For engineers, technicians, or buyers, understanding this component ensures better design, performance, and cost-efficiency in operations.