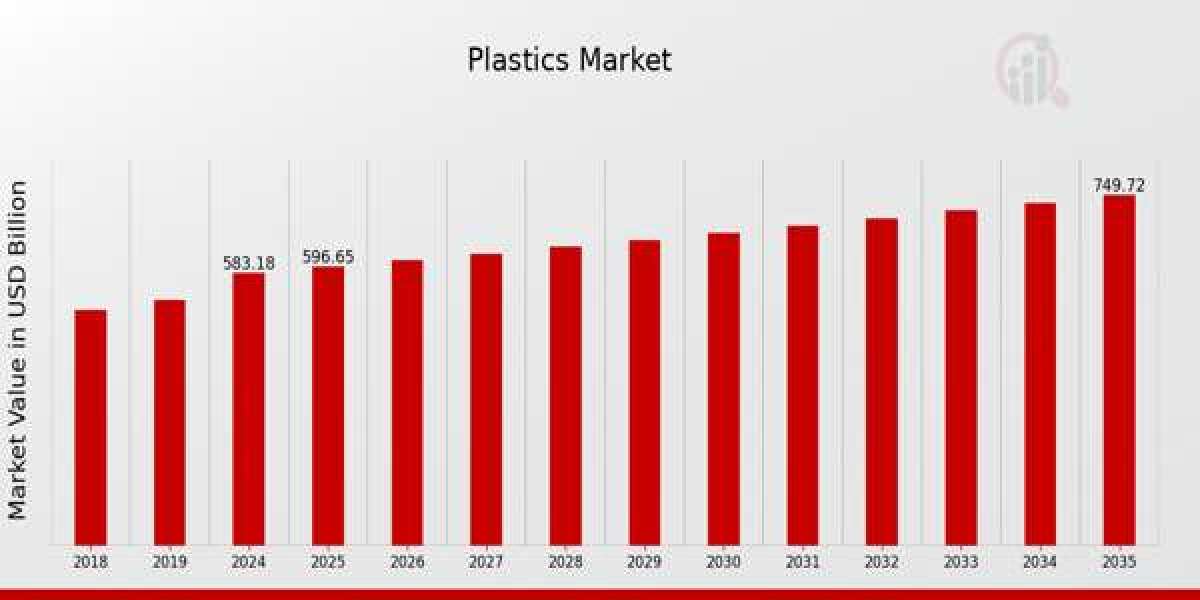
The plastics market plays a critical role in shaping modern industries and consumer lifestyles. As a versatile and durable material, plastic is used across nearly every sector—from packaging, automotive, and construction to electronics, healthcare, and agriculture. With its ability to be molded into countless forms and its wide range of properties, plastic has revolutionized product design and manufacturing on a global scale. The market for plastics has experienced significant growth over the decades and continues to evolve with technological innovations, environmental challenges, and shifting regulatory landscapes.
The global demand for plastics is primarily driven by its cost-effectiveness, strength, and adaptability. Products made from plastic tend to be lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to process. This makes them ideal for applications requiring efficiency, such as food packaging that extends shelf life or automotive components that reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. In construction, plastic materials such as PVC pipes and insulation products contribute to durability and energy conservation. The healthcare sector benefits from plastics in the form of medical devices, surgical instruments, and sterile packaging, where safety and hygiene are paramount.
One of the largest segments within the plastics market is packaging, accounting for a substantial portion of global consumption. The shift toward convenience products and ready-to-eat meals has significantly boosted the use of plastic packaging. Flexible packaging, in particular, has grown in popularity due to its lightweight nature and reduced transportation costs. Plastic bottles, containers, wraps, and films are now standard in both food and non-food packaging solutions. While this sector has seen continued growth, it also faces mounting pressure from consumers and governments to adopt more sustainable practices and materials.
The automotive industry also heavily relies on plastics for manufacturing various vehicle parts. From dashboards and bumpers to fuel systems and wiring insulation, plastic components contribute to weight reduction, fuel efficiency, and cost savings. As electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models gain market share, the demand for lightweight materials such as plastics is expected to rise further. These vehicles often require specialized components, including battery casings and thermal insulation, which plastic materials can efficiently fulfill.
In construction, plastics are widely used for their durability, weather resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Applications include window frames, pipes, roofing membranes, flooring, and insulation. The versatility of plastics allows architects and engineers to create innovative designs that are both energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. As building regulations increasingly emphasize sustainability and energy conservation, the use of advanced plastic materials in green buildings is expected to grow.
The electronics and electrical sector represents another critical area for plastic usage. The insulating properties of certain plastics make them ideal for cable sheathing, circuit boards, switches, and connectors. Plastics are also used in the casings of computers, smartphones, televisions, and home appliances. With the global surge in consumer electronics and smart devices, the demand for high-performance plastics with enhanced heat resistance and electrical insulation continues to rise.
Despite its numerous advantages, the plastics market faces significant challenges, particularly concerning environmental sustainability. The growing awareness of plastic pollution, especially in oceans and water bodies, has led to increased scrutiny of single-use plastics and inadequate waste management practices. Governments and environmental groups have called for reductions in plastic consumption, improved recycling infrastructure, and the development of biodegradable alternatives. Many manufacturers are now investing in circular economy models, which focus on recycling, reusing, and repurposing plastic products to minimize waste and environmental impact.
Innovation is key to the future of the plastics market. Research and development efforts are being directed toward bioplastics—plastics made from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, and vegetable oils. These materials offer the potential to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions. Additionally, advanced recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling and pyrolysis, are gaining traction. These methods break down plastics into their basic components, allowing for the creation of high-quality recycled materials suitable for demanding applications.
Regulatory developments across the world are also shaping the direction of the plastics market. Many countries have implemented bans or restrictions on certain types of plastic products, such as plastic bags, straws, and microbeads. Industry standards and environmental certifications are being revised to encourage sustainable practices. As a result, manufacturers are exploring ways to design products with easier recyclability and minimal environmental impact.