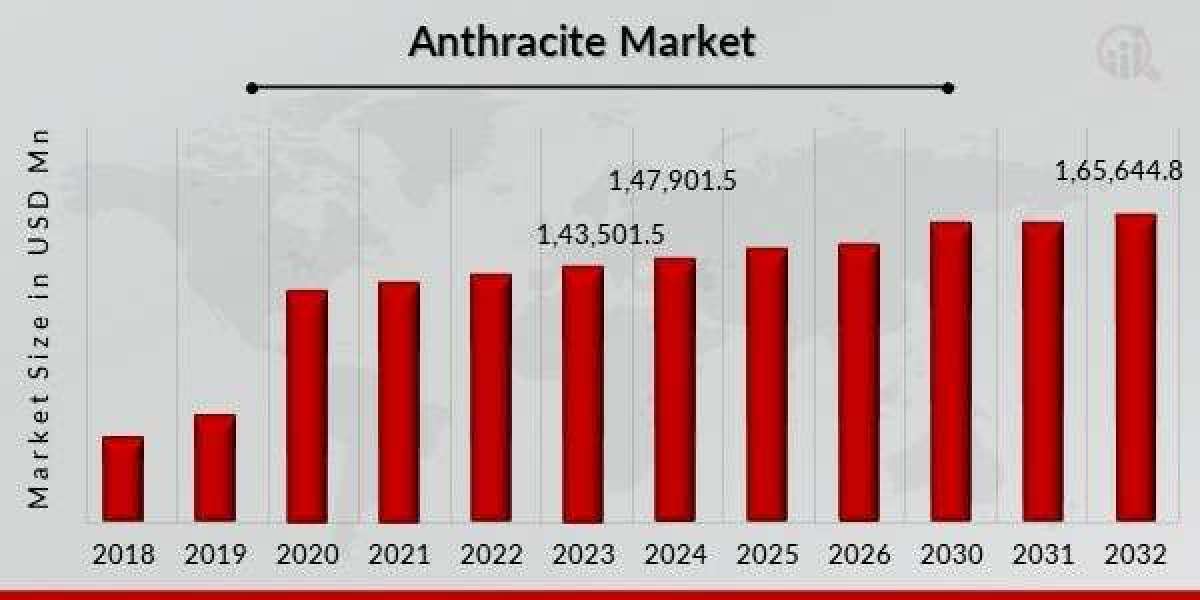
The anthracite market is an integral segment of the global coal industry, representing a premium quality coal type with high carbon content, low impurities, and superior calorific value. Anthracite, commonly referred to as hard coal, is characterised by its lustrous appearance and hardness compared to other types of coal such as bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite. It is known for its clean-burning properties, low volatile matter, and minimal smoke generation during combustion, making it highly suitable for applications demanding cleaner fuel and efficient heat output.
The market for anthracite is driven primarily by its extensive use in the steel and metallurgical industries. Anthracite serves as a reducing agent in steel manufacturing processes, especially in electric arc furnaces and blast furnaces, where it replaces coke to a certain extent due to its high fixed carbon and low sulphur properties. Its role in steel production is critical as industries continue to prioritise high-quality inputs for superior metal output and energy efficiency. Additionally, anthracite is used in the production of ferroalloys, non-ferrous metals, and foundries, further boosting its industrial demand globally.
Another major factor influencing the anthracite market is its use as a filtration media. Due to its high density and resistance to degradation, it is widely utilized in water purification and wastewater treatment plants to filter out impurities effectively. Municipal corporations and industrial units are adopting anthracite filtration systems to achieve stringent regulatory standards for potable and industrial water, contributing significantly to market growth. This trend is expected to expand further as environmental regulations tighten and industries enhance their sustainability and treatment processes.
The demand for anthracite is also rising in the energy sector. It is used in power generation in several regions, especially in Asia-Pacific countries, where anthracite-fired thermal power plants are operational. Its high calorific value provides efficient energy output, though its market share in power generation remains lower compared to bituminous coal due to its cost and availability constraints in some countries. Nonetheless, countries with domestic anthracite reserves continue to leverage this fuel to maintain energy security and reduce dependence on imported lower-grade coals.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is the largest consumer of anthracite, with countries like China, Vietnam, and Russia being major producers and exporters. China dominates both production and consumption due to its extensive steel and metallurgical industries, which require consistent anthracite supply to maintain operational efficiency and cost optimisation. Vietnam has emerged as an important exporter of anthracite, supplying high-quality grades to other Asian nations as well as global markets. Additionally, Russia’s anthracite production supports its domestic industrial fuel needs while also catering to export demands in Eastern Europe and Asia.
North America and Europe are other notable markets for anthracite. In the United States, anthracite reserves are largely concentrated in Pennsylvania, where it is used for residential heating, steel production, and filtration applications. Though its consumption has declined over the decades due to shifts towards natural gas and renewable energy, niche markets remain strong, particularly in domestic heating where anthracite is valued for its steady, long-lasting heat output. Europe imports significant quantities of anthracite for metallurgical purposes, with a focus on high-quality low-emission fuel to meet environmental standards imposed by regulatory bodies.
The market dynamics of anthracite are influenced by factors such as pricing volatility, mining regulations, environmental standards, and logistical considerations. Mining anthracite requires substantial capital investment and specialised extraction techniques due to its geological occurrence in hard seams. Additionally, strict environmental regulations on mining activities can impact production levels, while transportation infrastructure plays a critical role in cost and timely supply to end-users.
Sustainability trends are shaping the anthracite market as well. Industries are exploring ways to reduce carbon footprints and improve fuel efficiency, thereby increasing the attractiveness of anthracite over lower-grade coals that emit higher pollutants. Technological advancements in mining, beneficiation, and combustion systems are further supporting efficient utilisation of anthracite, enhancing its competitiveness in industrial applications.
However, the market faces challenges from the global transition towards renewable energy and decarbonisation targets set by countries under climate agreements. The long-term focus on reducing coal dependency is anticipated to impact overall coal markets, including anthracite. Yet, its indispensable role in metallurgy and industrial heating applications where alternatives remain limited ensures that demand will continue in these sectors for the foreseeable future.