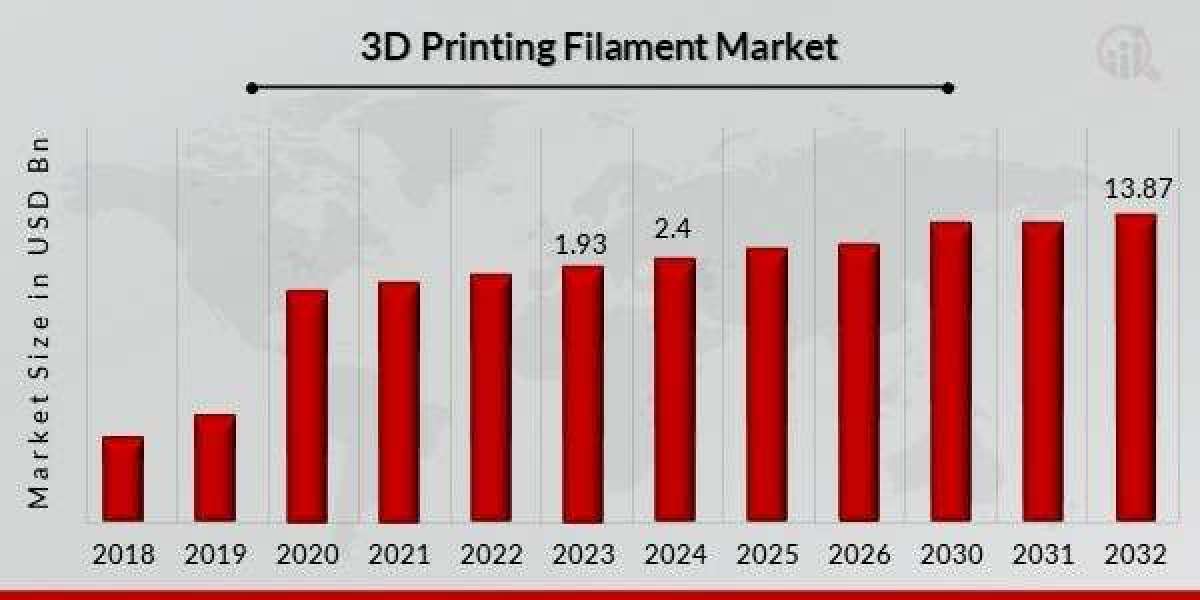
The 3D printing filament market has been witnessing significant growth over the years, driven by the increasing adoption of additive manufacturing technologies across various sectors globally. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionising production processes by enabling rapid prototyping, low-volume manufacturing, and the creation of complex geometries that were earlier difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods. Filaments are the backbone of fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printers, making the filament market a crucial segment within the overall additive manufacturing ecosystem.
The market for 3D printing filaments is expanding due to the rising demand for advanced and customized products in industries such as automotive, aerospace, healthcare, consumer goods, and education. Companies are investing in research and development to enhance filament properties, improve performance, and provide better material alternatives for specific industrial applications. The demand for filaments with enhanced mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability is particularly growing in aerospace and automotive industries where functional parts and engineering prototypes require durability and accuracy. On the other hand, filaments with high biocompatibility and non-toxicity are being preferred in the medical sector for manufacturing surgical models, dental implants, and prosthetics.
Polylactic acid (PLA) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are among the most commonly used 3D printing filaments in the market. PLA is widely used due to its biodegradability, low toxicity, ease of printing, and suitability for educational, hobbyist, and general prototyping purposes. Its availability in vibrant colours and low warping characteristics make it a popular choice for consumer and academic applications. ABS, on the other hand, offers higher strength and better temperature resistance, making it suitable for functional prototyping and end-use parts that require durability. However, ABS emits fumes during printing, which has led to a growing inclination towards filaments with less environmental and health impact.
The introduction of advanced filaments such as polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG), nylon, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), and carbon fibre reinforced filaments has further diversified the market. PETG combines the benefits of PLA and ABS, offering excellent strength, chemical resistance, and ease of printing without warping, thus gaining popularity in industrial and functional part manufacturing. Nylon filaments are preferred for their high strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, making them suitable for engineering applications that demand mechanical performance. TPU filaments provide flexibility and rubber-like properties, allowing the creation of elastic components such as seals, gaskets, and wearable prototypes.
Carbon fibre, glass fibre, and metal-filled filaments have also emerged as significant innovations in the market, enabling users to print parts with enhanced mechanical properties, lightweight characteristics, and metallic finishes. Carbon fibre infused filaments, in particular, are witnessing rising demand in the automotive and aerospace sectors due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity, which are ideal for functional prototyping and end-use parts requiring structural integrity.
With the evolution of material science, manufacturers are focusing on the development of specialty filaments to cater to specific industry requirements. For instance, flame retardant filaments are gaining traction in sectors where safety standards are stringent, such as electronics casings and automotive interiors. Conductive filaments are being used to produce electronic components, circuit boards, and sensor enclosures, expanding the applications of 3D printing into the field of electronics and embedded systems manufacturing. Metal-filled filaments containing bronze, copper, stainless steel, or aluminium particles are enabling the creation of aesthetic metallic-looking parts and low-load-bearing functional parts with ease of printing on standard FDM printers.
Geographically, the market is growing across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa. North America holds a significant share due to the strong presence of aerospace, defence, and healthcare industries adopting advanced 3D printing technologies. The region’s established ecosystem of additive manufacturing, combined with the high investment in research and innovation, contributes to the demand for high-performance filaments. Europe is also witnessing considerable growth owing to its automotive and aerospace giants integrating additive manufacturing for lightweighting and rapid prototyping. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK are leading contributors to the market growth in the European region.
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market for 3D printing filaments due to the rapid industrialisation, strong growth of the manufacturing sector, and increasing government support for adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India are investing in expanding their 3D printing capabilities to strengthen their manufacturing competitiveness. China, in particular, is experiencing growing consumption of filaments across automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods manufacturing, along with a strong base of filament manufacturers catering to domestic and global demand.