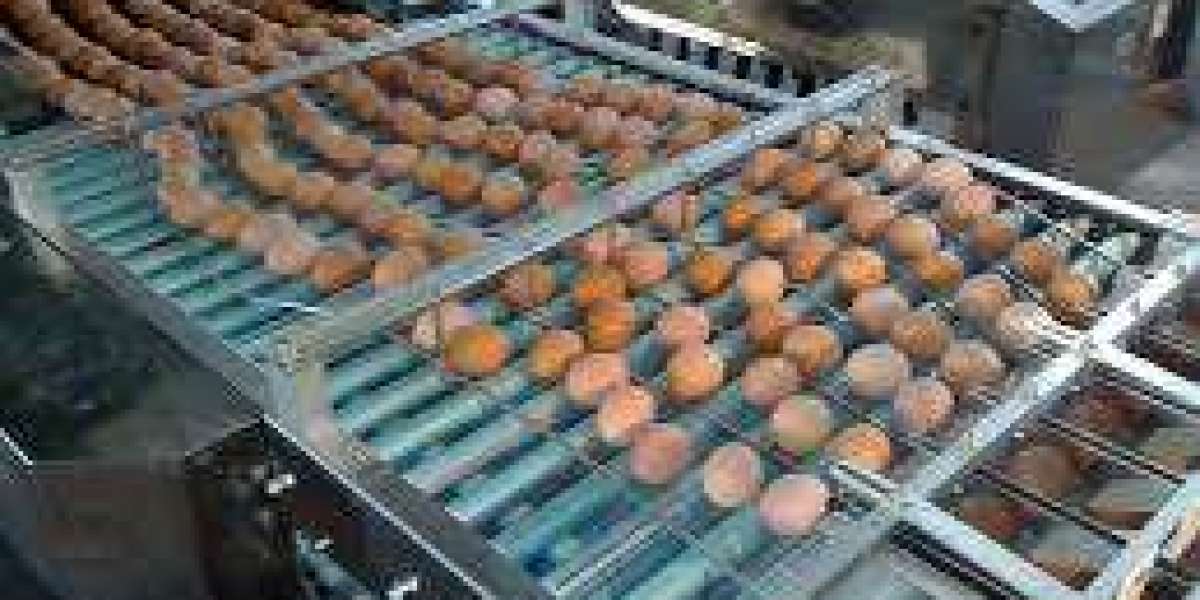
The egg collecting machine market is entering a modernization-led growth cycle as commercial poultry farms scale up, labor availability tightens, and producers seek more consistent egg quality, traceability, and biosecurity across high-throughput operations. Egg collecting machines automate the movement of eggs from laying points—most commonly conveyor belts in cage, barn, or aviary systems—to centralized collection, transfer, and pre-grading zones. By reducing manual handling, these systems help limit cracks, contamination, and breakage while improving labor productivity and enabling continuous collection schedules that align with modern farm management. Over 2025–2034, market growth is expected to be supported by expansion of industrial egg production capacity, upgrades to automated layer houses, and the increasing use of integrated solutions that connect egg collection with sorting, packing, palletizing, and data-driven farm monitoring.
Market overview and industry structure
The Egg Collecting Machine Market Size is valued at $149.3 Million in 2025. Worldwide sales of Egg Collecting Machine Market are expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 9.8%, reaching $ 288 Million by the end of the forecast period in 2032.
Egg collecting machines sit within the broader poultry house equipment ecosystem, closely linked to housing systems, feeding and drinking lines, climate control, manure removal, and downstream egg handling equipment. The market typically includes (1) in-house collection systems such as belt conveyors, cross conveyors, elevators, and egg transfer units; (2) central collection and accumulation systems that stage eggs for inspection or grading; and (3) control systems, sensors, and automation logic that regulate belt speeds, timing, and alarms. Depending on farm design, the equipment may be configured for cage-based layer houses or adapted to barn and aviary environments where egg flow and collection points differ.
Industry structure is anchored by poultry equipment OEMs and integrators that deliver full barn packages, specialized conveyor manufacturers, and regional installers/service partners. Many egg collecting machine projects are sold as part of new-build layer house investments, but a meaningful share comes from retrofit and upgrade programs—especially where farms expand capacity, convert layouts, or add automation to address labor pressure. Aftermarket revenue is significant in wear parts, belt replacements, rollers, motors, sensors, and service contracts, because uptime is critical and collection systems run daily under dust-heavy operating conditions. As a result, suppliers with strong local support, spare parts availability, and preventive maintenance capability tend to win repeat business.
Industry size, share, and market positioning
Egg collecting machines are a value-critical component even when they represent a modest share of total poultry house capex. The adoption rationale is driven by operational outcomes: fewer cracked eggs, reduced microbial risk from handling, higher throughput per worker, and smoother integration into grading and packing workflows. For large farms, the economics are strongly tied to volume and consistency—small reductions in breakage rates and labor hours can materially impact profitability at scale. For mid-sized farms, modular systems that can be expanded as capacity grows are particularly attractive, allowing producers to automate incrementally without a full facility rebuild.
Market share is shaped by system reliability, mechanical simplicity, gentle handling performance, and the ability to integrate seamlessly with housing layouts and downstream egg processing lines. Suppliers that can deliver end-to-end solutions—from in-house collection to transfer, washing (where applicable), grading, packing, and palletizing—often gain an advantage because integration risk is lower and accountability is clearer. However, in many regions, local installers and service partners heavily influence purchasing decisions because maintenance responsiveness and spare-part lead times matter as much as initial equipment cost.
Key growth trends shaping 2025–2034
A major trend is the accelerating shift toward higher automation density in layer houses. Producers are increasingly prioritizing “continuous flow” operations where egg collection, transfer, and staging are synchronized with grading and packing capacity, reducing bottlenecks and minimizing egg dwell time in warm environments. This supports adoption of smarter conveyor controls, accumulation tables, and automated diverters that keep lines running even during micro-stoppages.
Second, gentle handling and breakage reduction are becoming central differentiators. As retailers and foodservice buyers tighten quality expectations, farms focus on minimizing micro-cracks and shell damage. This drives upgrades in belt material quality, roller design, transfer angles, and speed control algorithms that reduce impacts and vibration during egg movement.
Third, integration with data and monitoring systems is expanding. Egg collecting machines increasingly incorporate sensors for belt speed, jam detection, egg flow rates, motor load, and system downtime. These data streams are being used for preventive maintenance, performance benchmarking between houses, and traceability workflows—especially when integrated with farm management platforms that also track flock health, feed conversion, and environmental conditions.
Fourth, biosecurity and hygiene-by-design are influencing equipment choices. Farm operators are looking for designs that reduce dust build-up, simplify cleaning, and isolate contamination risks between zones. Better guarding, enclosed transfer points, and easy-access cleaning features are being prioritized in new installations, particularly in regions where disease outbreaks increase risk sensitivity.
Finally, retrofit demand is rising. Many farms built in earlier expansion cycles are upgrading collection systems to improve efficiency without fully rebuilding housing. Modular conveyor upgrades, improved elevators, and more robust transfer systems are being deployed to support capacity expansion and reduce labor dependency.
Core drivers of demand
Labor availability and cost are among the strongest demand drivers. Egg collection is repetitive and time-sensitive; automation reduces dependence on manual tasks while improving consistency. The second driver is scale expansion in commercial egg production. As integrated producers and large farms increase flock size and build additional houses, automation becomes a practical necessity to keep operating complexity manageable.
Quality and loss reduction is another powerful driver. Breakage, micro-cracks, and contamination can quickly erode margins, especially when eggs are sold into premium retail or processed channels with strict acceptance criteria. Automated collection reduces human handling points and provides more stable flow to downstream sorting and packing systems.
A fourth driver is operational resilience. Automated collection systems support predictable throughput and allow farms to maintain output even when staffing is constrained or when farms adopt tighter biosecurity protocols that limit personnel movement. Finally, capital efficiency matters: modern collection systems can enable higher house productivity, better layout utilization, and improved integration with grading and packing lines, which helps justify automation investments over multi-year operating cycles.
Challenges and constraints
Despite strong demand, the market faces constraints that shape adoption pace and vendor selection. Upfront capex sensitivity remains significant, particularly for small and mid-sized producers in price-competitive egg markets. Buyers often require clear payback logic tied to labor savings and reduced breakage, and financing conditions can influence project timing.
Uptime and maintenance complexity are major operational risks. Egg collecting machines operate in harsh environments with dust, feathers, humidity, and continuous vibration; belt wear, misalignment, roller failures, and motor issues can cause downtime that directly affects daily collection. As a result, buyers prioritize robustness, easy maintenance access, and dependable service coverage.
Layout and integration complexity also matters. Collection systems must match housing type (cage, barn, aviary), building geometry, and downstream plant placement. Poor integration can create transfer bottlenecks, jams, or excessive egg impacts. Additionally, hygiene and biosecurity requirements can add design constraints, requiring segregated zones and cleaning-friendly materials.
Finally, variability in regional animal welfare standards can influence demand patterns. As farms transition housing formats, collection designs must adapt, and retrofit complexity can rise—creating longer sales cycles and greater engineering requirements for suppliers.
Browse more information
https://www.oganalysis.com/industry-reports/egg-collecting-machine-market
Segmentation outlook
By housing system, cage-based layer houses remain a major installed base in many regions, supporting high-volume demand for belt conveyors and centralized transfer systems, while barn and aviary systems drive demand for collection designs that manage more distributed egg flow and different transfer points. By automation level, basic collection systems remain widespread, but higher-growth demand is expected for integrated solutions that combine collection, accumulation, monitoring, and direct interfacing with grading/packing lines. By farm scale, large commercial complexes drive the majority of value due to multi-house installations and centralized egg handling infrastructure, while mid-sized farms increasingly adopt modular solutions that enable stepwise automation.
Key Market Players
- Big Dutchman
- Salmet
- Vencomatic Group
- Facco
- Hellmann Poultry
- SKA
- VDL Agrotech
- Jansen Poultry Equipment
- Henan Jinfeng Poultry Equipment
- Hebei Weizhengheng Animal Husbandry Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd.
- Guangzhou Huanan Poultry Equipment
- Techin Systems
- Munters
- Roxell
- Big Herdsman Machinery
Competitive landscape and strategy themes
Competition is shaped by reliability, gentle handling performance, integration capability, and service strength. Suppliers differentiate through durable conveyor components, optimized transfer geometries that reduce impact stress, smarter control systems that detect jams early, and remote support that improves uptime. Through 2034, strategic priorities are likely to include expanding retrofit-friendly product lines, offering integrated “collection-to-packing” solutions, building stronger local service ecosystems, and embedding monitoring features that support predictive maintenance and operational benchmarking.
Partnerships between poultry housing integrators, automation providers, and downstream egg processing equipment suppliers are expected to intensify because producers increasingly want turnkey solutions with clear accountability for performance. Vendors that can simplify installation, reduce commissioning time, and provide long-term service confidence will capture a growing share in expansion-heavy regions.
Regional dynamics (2025–2034)
Asia-Pacific is expected to be a major growth engine as industrial egg production expands, new large-scale layer complexes are built, and producers adopt automation to manage labor pressure and improve consistency; modernization of poultry infrastructure and rising demand for packaged eggs support adoption of integrated egg handling lines. North America is likely to see steady growth driven by upgrades to high-throughput facilities, replacement of aging conveyor systems, and increasing focus on uptime, biosecurity, and integration with automated grading and packing. Europe is expected to maintain robust demand shaped by strong emphasis on welfare-led housing systems, hygiene, and traceability; this supports investment in advanced collection designs suited to barn/aviary formats and in monitoring features that document performance and downtime. Latin America offers meaningful upside as commercial egg capacity expands and integrators modernize facilities, though price sensitivity and service coverage can influence equipment choices and automation depth. Middle East & Africa growth is expected to be selective but improving, led by investments in food security, local poultry production expansion, and new farm builds in key hubs; adoption will depend on financing availability, reliable installation partners, and the ability to maintain equipment performance in hot, dust-heavy environments.
Forecast perspective (2025–2034)
From 2025 to 2034, the egg collecting machine market is positioned for steady growth as poultry producers scale operations and pursue higher automation to stabilize labor needs, reduce losses, and improve quality consistency. The market’s center of gravity shifts toward integrated, monitoring-enabled collection systems that connect smoothly into grading and packing lines and support predictable daily throughput. Growth will be strongest where new layer capacity is built, where modernization programs replace aging conveyors, and where biosecurity and traceability requirements raise the value of controlled, low-handling egg flow. By 2034, egg collecting machines are likely to be viewed not just as mechanical conveyors but as reliability-critical production infrastructure—optimized for gentle handling, high uptime, and data-driven farm operations.
Browse Related Reports
https://www.oganalysis.com/industry-reports/plant-growth-regulators-market
https://www.oganalysis.com/industry-reports/controlled-release-fertilizer-market
https://www.oganalysis.com/industry-reports/milking-automation-market
https://www.oganalysis.com/industry-reports/egg-collecting-machine-market
https://www.oganalysis.com/industry-reports/egg-sorting-machine-market