Introduction
Asset-intensive organizations are under mounting pressure to do more with less. Downtime directly impacts revenue. Aging assets demand higher maintenance spend. At the same time, enterprises must align operational reliability with digital transformation, sustainability goals, and customer expectations.
This is why Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) is undergoing a fundamental shift. Vendors are converging EAM with Asset Performance Management (APM), Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) to create unified, intelligence-driven ecosystems. Instead of reacting to failures, organizations can now predict, prevent, and optimize asset performance across the enterprise. The SPARK Matrix™: Enterprise Asset Management by QKS Group captures how this evolution is reshaping the competitive landscape and redefining asset-centric value creation.
Market / Industry Overview
Enterprise Asset Management refers to the systems and processes used to manage physical assets throughout their lifecycle—from design and acquisition to operation, maintenance, and retirement. Traditionally, EAM platforms focused on maintenance scheduling, work orders, and spare parts tracking.
Today, EAM has expanded into a strategic operational layer that connects asset health with production efficiency, supply chain performance, and financial planning. By integrating with APM, MES, and ERP, modern Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) platforms provide end-to-end visibility across IT and OT environments.
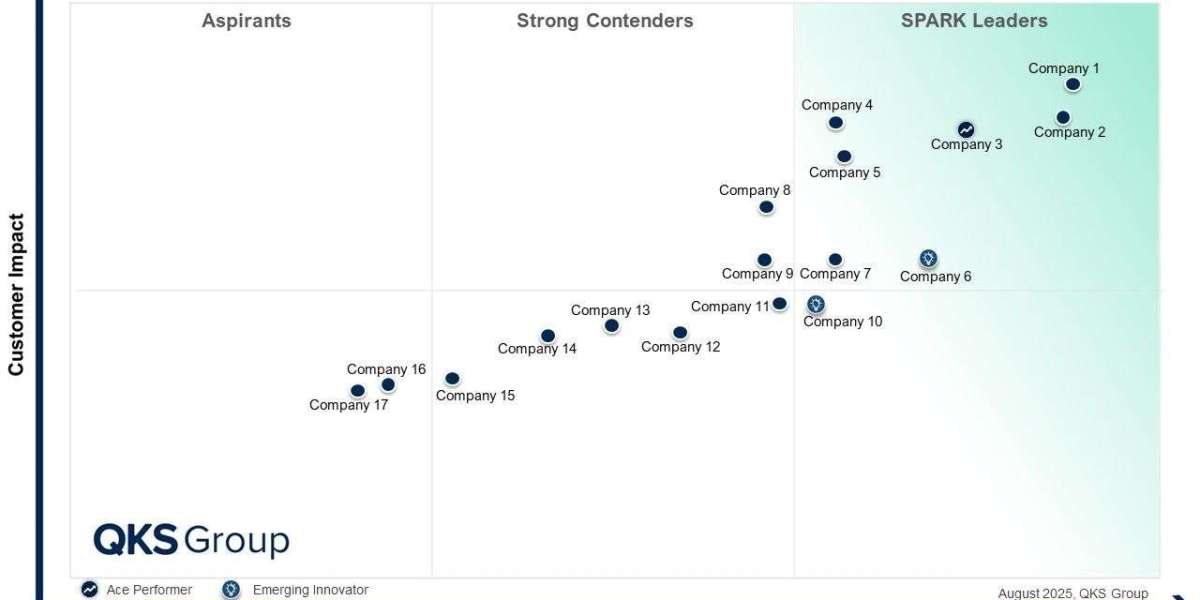
In the SPARK Matrix: Enterprise Asset Management, QKS Group evaluates 16 leading vendors:
- Accruent
- Aptean
- Brightly Software
- eMaint
- Eptura
- Hexagon
- Hitachi Energy
- IBM
- Ideagen Devonway
- IFS Ultimo
- MaintainX
- Pragma
- Ramco Systems
- SAP
- ServiceNow
- Upkeep
Each vendor is assessed across technology excellence and customer impact, delivering a balanced, comparative view of solution maturity, innovation, and real-world value.
Key Challenges Businesses Face
Despite increased investment in asset management platforms, organizations continue to face several structural challenges.
Reactive Maintenance Culture
Many enterprises still rely on corrective or time-based maintenance, leading to unexpected failures and higher operating costs.
Disconnected Systems and Data Silos
EAM, MES, ERP, and condition-monitoring tools often operate independently, preventing holistic visibility into asset performance and its business impact.
Limited Predictive Capabilities
Without advanced analytics and real-time data integration, asset insights remain backward-looking rather than predictive.
Workforce and Adoption Barriers
Complex interfaces, limited mobile access, and insufficient change management hinder technician adoption and productivity.
Scalability Across Global Operations
Standardizing asset strategies across plants, regions, and asset classes remains difficult, especially for organizations with legacy infrastructure.
Key Trends & Innovations
The EAM market is being reshaped by convergence, intelligence, and usability.
EAM–APM–MES–ERP Convergence
Leading vendors are integrating reliability, production, and financial data to enable closed-loop decision-making across operations.
Predictive Analytics and AI
Machine learning models analyze sensor data, maintenance history, and operating conditions to forecast failures and optimize maintenance strategies.
IIoT and Digital Twin Adoption
Digital twins simulate asset behavior, allowing teams to test scenarios, optimize maintenance intervals, and reduce operational risk.
Cloud-Native and SaaS Platforms
Cloud-based EAM solutions improve scalability, accelerate deployment, and reduce infrastructure overhead.
Mobile-First Design
Technician-centric mobile applications improve work execution, data capture, and workforce efficiency across distributed environments.
Benefits & Business Impact
When deployed as part of a connected ecosystem, Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) delivers measurable business outcomes.
- Reduced unplanned downtime through predictive maintenance
- Lower maintenance and inventory costs via optimized planning
- Extended asset life and improved capital utilization
- Improved operational visibility across assets, plants, and regions
- Faster decision-making through real-time analytics
- Stronger compliance and audit readiness
Beyond cost savings, modern EAM platforms enhance operational resilience and enterprise agility.
Use Cases or Real-World Examples
Manufacturing
Manufacturers integrate EAM with MES to align maintenance with production schedules, improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Energy and Utilities
Utilities use EAM and APM to monitor grid assets, predict failures, and ensure regulatory compliance across critical infrastructure.
Transportation and Logistics
Rail, aviation, and fleet operators leverage EAM platforms to enhance safety, reliability, and asset availability.
Facilities and Infrastructure
Enterprises manage geographically dispersed facilities using mobile EAM solutions to meet service-level and compliance requirements.
How Organizations Can Choose the Right Solution
Selecting the right Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) platform requires a strategic, long-term perspective.
Key evaluation criteria include:
- Depth of asset lifecycle and maintenance capabilities
- Native support for predictive analytics and APM
- Ease of integration with ERP, MES, and OT systems
- Deployment flexibility (cloud, hybrid, on-premises)
- Mobile usability and workforce adoption
- Vendor roadmap, ecosystem, and customer support
The SPARK Matrix provides a transparent framework to compare vendors across these dimensions and align selection with business priorities.
Future Outlook (2025–2028)
From 2025 to 2028, EAM will continue evolving into a system of operational intelligence.
Key developments will include:
- Greater automation in maintenance planning and scheduling
- Expanded use of AI-driven diagnostics and recommendations
- Deeper IT–OT convergence across enterprise operations
- Increased focus on sustainability, energy optimization, and ESG reporting
- EAM platforms expanding into broader service and operations management
Asset management will become increasingly predictive, autonomous, and business-aligned.
Conclusion
Enterprise Asset Management is no longer confined to maintenance execution. It is becoming a strategic enabler of operational excellence, resilience, and enterprise-wide value.
As highlighted in the SPARK Matrix: Enterprise Asset Management, vendors that successfully converge EAM with APM, MES, and ERP are setting new benchmarks for predictive operations. For technology buyers and enterprise leaders, modern EAM platforms represent a critical foundation for future-ready, asset-driven organizations.