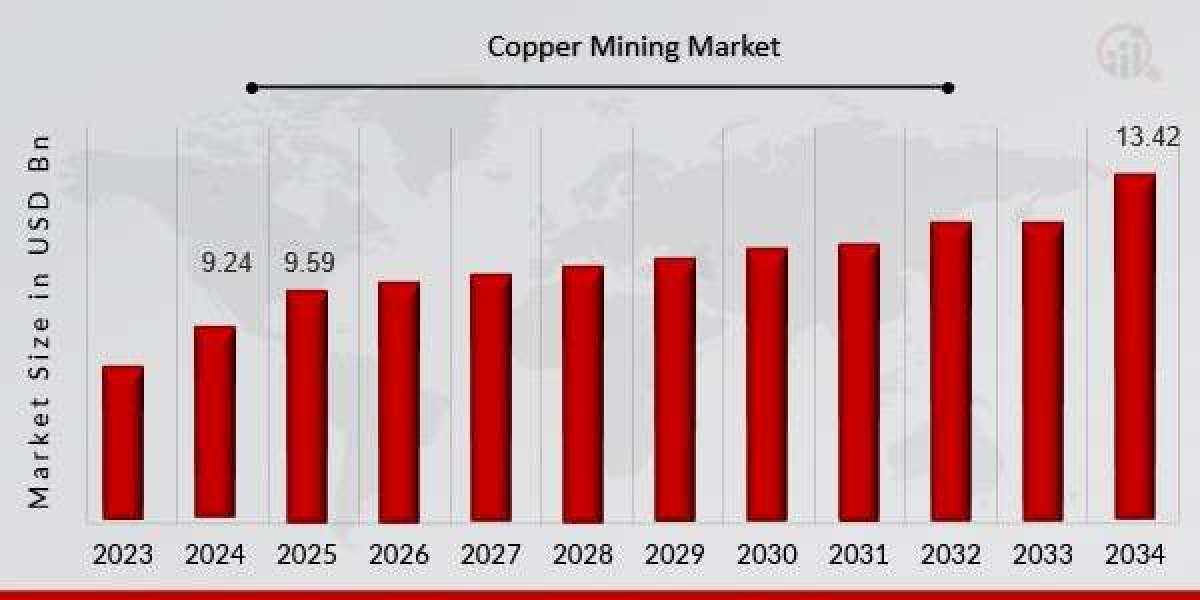
The Copper Mining Market is a cornerstone of the global mining industry, playing a vital role in supporting industrial growth, technological innovation, and the transition to cleaner energy systems.
At the heart of this market are large-scale mining operations, concentrated in countries rich in copper reserves such as Chile, Peru, China, the United States, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. These nations account for the majority of global copper output, feeding the raw material needs of both emerging and developed economies. Chile remains the world’s top copper producer, with extensive mines like Escondida and Collahuasi, while new exploration and mining projects continue to emerge in other resource-rich regions, aiming to meet the growing global appetite for copper.
The copper mining industry is influenced by a variety of global factors including infrastructure development, urbanization, electric vehicle (EV) adoption, and the expansion of renewable energy installations. Copper is essential in the production of EV batteries, charging infrastructure, solar panels, wind turbines, and smart grids. As governments and industries push toward low-carbon economies, the demand for copper is expected to grow significantly over the next few decades. Analysts predict that copper consumption will surge due to the electrification of transportation and clean energy investment, placing immense pressure on mining companies to ramp up production and explore new reserves.
However, the market is not without its challenges. Fluctuating copper prices driven by global supply-demand imbalances, geopolitical instability in mining regions, rising operational costs, and stringent environmental regulations create complex conditions for miners. Additionally, the depletion of high-grade ores means companies now have to extract copper from deeper or more remote locations, increasing the technical difficulty and cost of operations. These factors are prompting mining firms to adopt more sustainable and technologically advanced methods to optimize extraction and reduce environmental impacts.
Sustainability is becoming a key focus area in the copper mining sector. With environmental concerns at the forefront, mining companies are investing in cleaner technologies, water recycling systems, energy-efficient equipment, and tailings management to reduce their ecological footprint. The use of automation, AI, and digital monitoring is improving operational efficiency and safety in mines, while also lowering emissions. Furthermore, the concept of “green copper,” where production adheres to strict environmental and ethical standards, is gaining traction among consumers and industries aiming to build greener supply chains.
Copper recycling also plays a significant role in supplementing primary copper production. Secondary copper, derived from the recycling of scrap materials like wiring and plumbing, provides a more sustainable and energy-efficient alternative. The recycling market not only helps meet demand but also reduces the pressure on natural resources and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. In regions where mining activity is limited, recycling offers a viable source of copper for industrial and manufacturing use.
Copper is an essential metal known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability, making it indispensable in sectors such as construction, electronics, power generation, telecommunications, transportation, and renewable energy. As economies expand and modernize, the demand for copper continues to rise, positioning the copper mining sector as a critical engine of economic development.