The smart agriculture solution market is increasingly focused on enabling climate-resilient farming and reducing risks associated with weather variability, resource scarcity, and production uncertainty. Climate change has intensified challenges such as droughts, floods, unpredictable rainfall, and pest outbreaks, directly impacting agricultural productivity worldwide. Smart agriculture solutions leverage digital tools, data-driven insights, and automation to help farmers anticipate risks, adapt practices, and maintain stable yields under changing environmental conditions.
Climate Change Impact On Modern Agriculture
Agriculture is one of the most climate-sensitive sectors, with productivity closely tied to weather patterns and natural resources.
Rising temperatures, shifting rainfall cycles, and extreme weather events disrupt planting schedules, crop growth, and harvest timing. These changes increase yield volatility and economic uncertainty for farmers. Traditional farming methods often lack the flexibility required to adapt to these conditions, driving the need for advanced smart agriculture solutions that support proactive decision-making and risk mitigation.
Role Of Smart Agriculture In Climate Resilience
Smart agriculture integrates digital technologies to enhance farm adaptability and resilience.
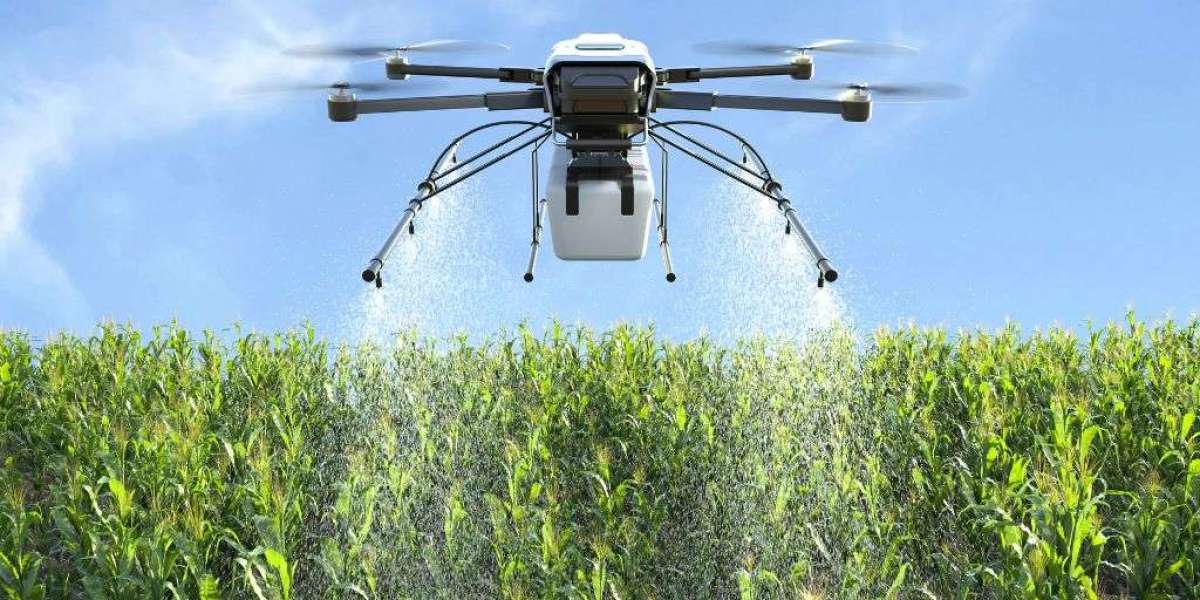
Sensors, connected equipment, and data platforms enable continuous monitoring of environmental conditions such as soil moisture, temperature, and humidity. These systems provide early warnings of drought stress, frost risk, or excessive rainfall, allowing farmers to adjust irrigation, planting, or crop protection strategies in real time. Climate-resilient farming supported by smart solutions improves yield stability and reduces losses caused by unpredictable weather.
Predictive Analytics And Weather Forecasting
Advanced analytics play a crucial role in managing climate-related risks.
Smart agriculture platforms use historical data, satellite imagery, and real-time weather inputs to generate accurate forecasts and predictive insights. These tools help farmers anticipate extreme weather events and plan preventive measures such as altering planting dates, selecting resilient crop varieties, or adjusting fertilizer schedules. Predictive analytics improves preparedness, minimizes damage, and enhances operational efficiency across farming operations.
Smart Irrigation And Water Management
Water scarcity is a growing concern in many agricultural regions.
Smart irrigation systems use soil moisture sensors, weather data, and automated controls to optimize water usage. Instead of relying on fixed irrigation schedules, these systems deliver water precisely when and where it is needed. Efficient water management reduces drought risk, conserves resources, and supports sustainable crop growth, especially in regions facing increasing water stress due to climate change.
Crop Monitoring And Stress Detection
Early detection of crop stress is essential for climate-resilient farming.
Remote sensing technologies, including drones and satellite imaging, monitor crop health across large areas. These tools identify early signs of heat stress, nutrient deficiencies, or disease outbreaks triggered by changing climate conditions. Timely intervention reduces yield losses and improves crop resilience, enabling farmers to respond effectively to environmental challenges.
Diversification And Adaptive Farming Practices
Smart agriculture solutions support adaptive farming strategies that enhance resilience.
Digital platforms provide insights into crop diversification, rotation planning, and variety selection based on climate data and soil conditions. Diversified cropping systems reduce dependency on single crops and lower vulnerability to climate-related shocks. Technology-enabled decision support helps farmers adopt adaptive practices that improve long-term sustainability and economic stability.
Automation And Labor Risk Reduction
Climate variability often increases labor challenges during peak farming periods.
Automation technologies such as autonomous tractors, robotic harvesters, and smart machinery reduce reliance on manual labor. Automated systems ensure timely field operations even under adverse weather conditions, minimizing delays and productivity losses. Labor efficiency supported by automation enhances resilience and operational continuity in climate-sensitive environments.
Insurance And Financial Risk Management Integration
Smart agriculture solutions are increasingly integrated with financial risk management tools.
Data collected from farms supports precision insurance models and risk assessment frameworks. Accurate farm-level data enables better evaluation of climate risks, facilitating fair insurance pricing and faster claim processing. These integrations improve financial protection for farmers, reducing economic uncertainty caused by climate-induced losses.
Regional Adoption And Market Expansion
Adoption of climate-resilient smart agriculture solutions varies across regions.
Developed economies prioritize advanced analytics, automation, and digital platforms to enhance climate adaptation. Emerging economies focus on affordable sensor-based solutions, mobile advisory services, and water-efficient technologies. Government support, international partnerships, and technology transfer initiatives are accelerating adoption across climate-vulnerable regions, expanding the global smart agriculture solution market.
Challenges In Implementing Climate-Resilient Technologies
Despite strong potential, adoption challenges remain.
High initial costs, limited digital infrastructure, and lack of technical knowledge hinder implementation in some regions. Addressing these challenges requires capacity-building programs, financial incentives, and localized solution development. Collaboration between governments, agritech providers, and farming communities is essential to ensure inclusive and scalable adoption.
Future Outlook
The future of climate-resilient farming depends on continued innovation and integration of smart agriculture solutions.
Advancements in artificial intelligence, remote sensing, and edge computing will enhance predictive accuracy and real-time responsiveness. As climate risks intensify, demand for resilient farming technologies will grow, positioning smart agriculture as a critical pillar of global food security and sustainable development.
Conclusion
Climate-resilient farming is no longer optional in modern agriculture. Smart agriculture solutions provide the tools needed to anticipate risks, adapt practices, and maintain productivity under changing environmental conditions. By combining technology, data, and adaptive strategies, farmers can mitigate climate risks and build sustainable agricultural systems capable of meeting future food demands.